Holang modular nitrogen generator to assist laser cutting industry
发布时间:2023-10-16 浏览次数:2731
With the popularization of Holang modular nitrogen generator products and the praise of users, last week we reached a matching cooperation with a laser cutting manufacturer for foreign projects. Compared with the traditional PSA nitrogen maker, the modular nitrogen generator has high nitrogen production efficiency ,no pressure vessels, and the export of the equipment does not require container inspection, in addition, it also avoids the problem of high price and long delivery time of the export container.

As we all know, galvanized steel plate is a kind of plate that protects the carbon steel inside through the surface galvanized, and is not easy to rust for long-term use. Although this plate will be slightly more expensive than ordinary carbon steel plate, there is no need to spray and other post-process in order to prevent rust.in the actual production process, the figure of galvanized plate can be seen everywhere. There are three cutting processes for galvanized steel: air cutting, oxygen cutting and nitrogen cutting. Let's first analyze the advantages and disadvantages of these three cutting processes:

Air cutting: the advantage is that the processing cost is very low, only need to consider the laser itself and the electricity costs of the air compressor, no auxiliary gas costs, the cutting efficiency on the sheet can be matched by nitrogen cutting, is an economic and efficient cutting method. But the disadvantages on the cutting surface are equally obvious. First of all, the air cutting section will produce underside burrs, and the products after laser processing must also go through secondary processing such as deburring, which is not conducive to the entire product production cycle. Secondly, the air cut section is easy to black, affecting the quality of the product. Therefore, the advantages of laser processing without subsequent treatment can not be reflected, so in the processing of galvanized steel plates, many companies are not willing to choose air cutting methods.
Oxy-fuel cutting: This is the most traditional and standard cutting method. The advantage is that it does not require frequent switching of auxiliary gases, making it easier for factory management, especially in sheet metal processing with carbon steel as the main material. However, the drawback is that after oxy-fuel cutting, there will be a layer of oxide scale on the cut surface. If products with this oxide scale are directly welded, over time, the oxide scale will naturally peel off. This is one of the reasons why welding galvanized plates is prone to incomplete fusion.

Auxiliary gas corresponding to different processing materials:
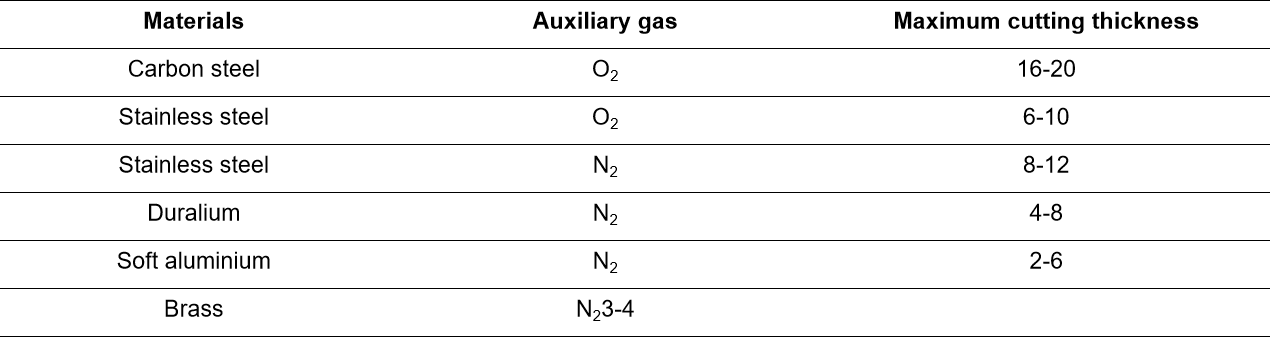
In actual production, air pressure and nozzle determine the roughness of the section. Appropriate increase of air pressure is conducive to slag discharge, but too large will increase roughness. Nitrogen does not participate in combustion and is used to blow away liquid materials with a relatively low temperature, requiring a high pressure of 10 to 14 bar. Nozzle nitrogen uses high pressure and requires a large nozzle diameter to ensure the output volume.
Nitrogen purity has a great influence on cutting quality, as shown in the following table
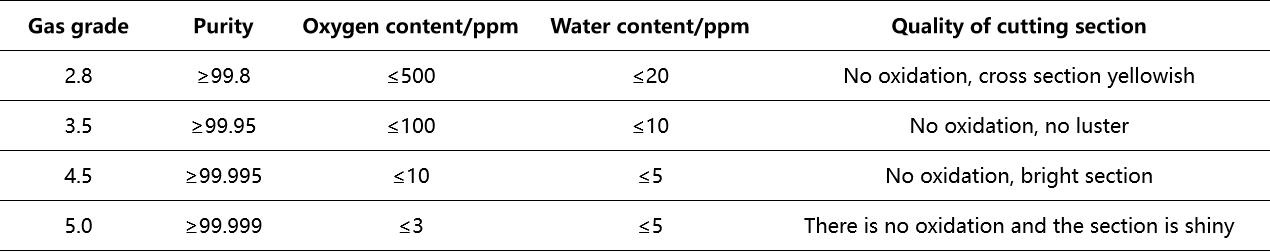
Nitrogen cutting solves many processing problems in actual production, and expands the processing scope to aluminum, brass and other areas where oxygen cutting is difficult to process.
Carbon steel is mainly cut with oxygen, and the surface temperature is very high because of carbon-assisted melting and oxygen-assisted combustion. When cutting the hole with sharp Angle and diameter less than the material thickness, too much heat is concentrated in the narrow area, and the cutting quality cannot be guaranteed. Nitrogen does not assist combustion, and has a cooling effect, is suitable for solving such processing problems, can improve product quality.
The proportion of stainless steel containing high alloying elements such as Ni is large, the melt viscosity is large, the fluidity is poor, and the low air pressure during oxygen cutting is easy to lead to quality defects such as sticky slag. When welding stainless steel, the oxide layer seriously affects the welding quality, especially argon arc welding. The protective effect of nitrogen during nitrogen cutting can produce a high-quality no-oxidation section, which meets the high requirements of stainless steel welding parts for cutting sections. Moreover, the high air pressure during nitrogen cutting can easily overcome the above quality defects. Nitrogen cutting is suitable for processing stainless steel parts with welding requirements or high added value.
Aluminum and brass have high reflectivity and low absorptivity to lasers, requiring high power to melt materials. And it should be equipped with a reflection absorption device, so that the horizontal linear wave does not reflect back to the lens, protect the safety of the laser, and require nitrogen cutting. Aluminum has a low melting point and can be cut with oxygen below 3 mm, but the quality is poor, the section is rough and the burr is hard. The nitrogen cutting section is smooth, and no burrs can be obtained below 4 mm. Aluminum is viscous, coupled with good thermal conductivity, the melt may not have time to blow away has cooled, so prone to burrs. Improve the finish by adjusting the focus, increasing the pressure, and decreasing the speed, at least to ensure that the burrs can be easily removed.
In addition, as a special cutting, the energy is only 5% of the basic power, and it only acts on the surface of the material. Mainly used to etch marks. Oxygen etching temperature is high, sometimes there is slag on the surface, and concentrated etching will damage the surface of the part due to heat accumulation. Nitrogen etching is bright and does not damage the surface, and can be used to etch demanding captions.
The cooling and protective effect of nitrogen can improve the cutting quality and provide a high quality oxidation free section for stainless steel materials. The processing scope has also been expanded to aluminum, brass and other areas that cannot be processed by oxygen cutting. Nitrogen cutting has achieved good results in practical application and solved many processing problems, but it also has the defect of high cost. It can also process wood, plexiglass and other special materials without auxiliary combustion, and has broad application prospects.
