The application of nitrogen as a "carrier gas" in laboratory analysis and testing instruments.
发布时间:2024-09-20 浏览次数:713
Introduction
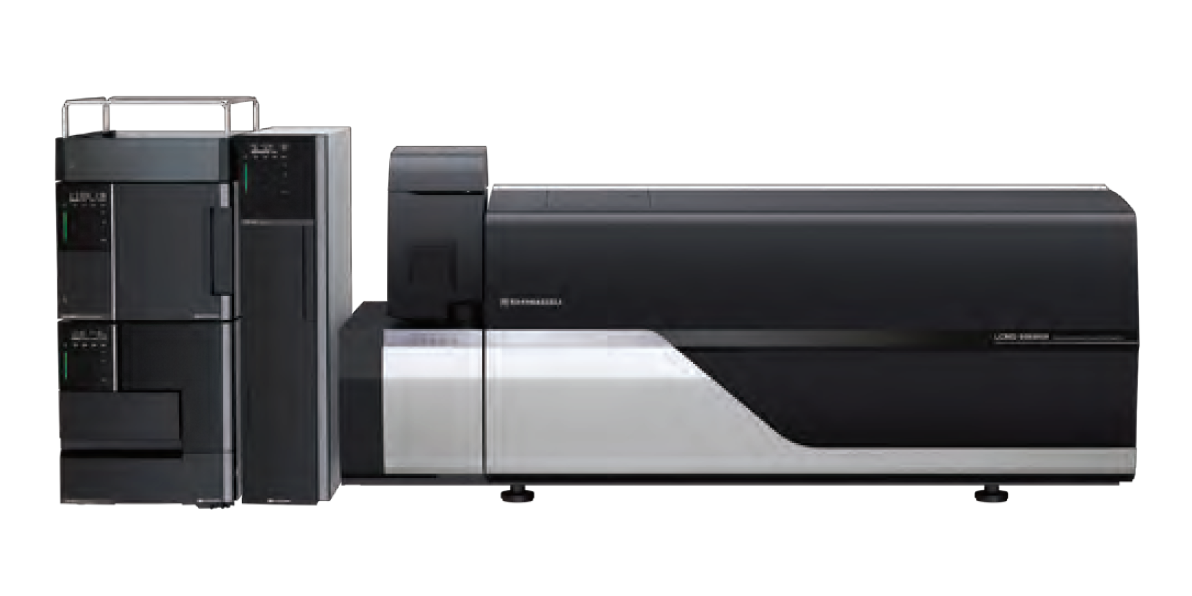
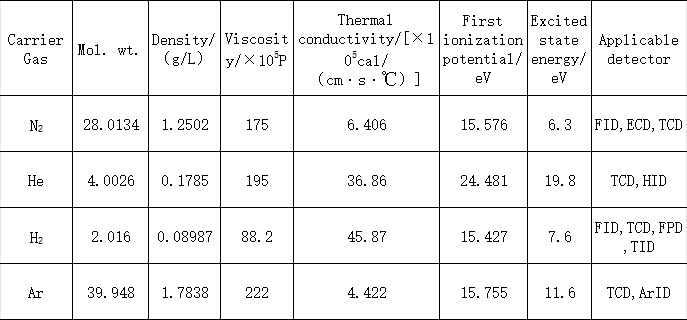
One of the most common applications of nitrogen in laboratories is to provide a stable inert gas environment for analytical instruments such as gas chromatographs, liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS), and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). As an inert gas, nitrogen does not react with most substances, making it an ideal protective atmosphere for detectors, enhancing their sensitivity and improving the accuracy of trace component measurements. In addition to serving as a protective atmosphere for detectors, nitrogen also plays a crucial role as a carrier gas for transporting samples in analytical instruments.
01

02

03

Holang Technology
continuously develops in the direction of intelligence, environmental friendliness, energy efficiency, and customization,
committed to providing laboratories
with more efficient, convenient, and safe gas supply solutions.

(Facebook)